|
International symposium Web-based smoking cessation aids for young people - Berlin - 2008 |
|
|
The Smoking Prevention Program of feelok |
|
Padlina Oliver - Jimmy Gerda - Bauer Georg - Gutzwiller Felix |
|
Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine, University of Zurich
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
A few months ago, we got a grant from the Tobacco Control Fund to develop the new version of the smoking prevention program and this symposium is a great opportunity to learn from the experience of other experts, who are active in the same field.
|
|
|
|
|
For the first 15 minutes I will talk about feelok, in the second half of my presentation, I'll speak about the smoking prevention program and point out our main scientific findings in this field.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
feelok is a multidimensional website. It covers the topics alcohol, job, physical activity, cannabis, nutrition, sexuality, smoking, self esteem and self confidence, stress and suicide. For no single institution in Switzerland alone, is it possible to manage a website which covers so many themes. For this reason …
|
|
|
|
|
… feelok is also a multiinstitutional project. This means 34 institutions in Switzerland as well as in Austria are responsible for the updates and correctness of the content, for the dissemination, the evaluation and the sponsoring of the internet program
|
|
|
|
|
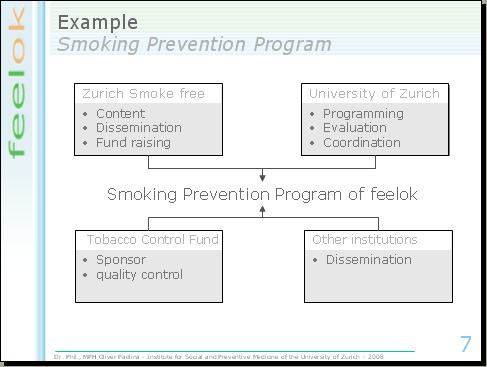
An example: The organisation "Zurich smoke free" is responsible for the content, the dissemination and the fund raising of the Smoking prevention program. The University of Zurich is in charge of the programming and the evaluation of the smoking prevention program and is responsible for the coordination of the network of feelok. The tobacco control fund finances the development of new tools for the smoking prevention program and verifies the quality of our product. Other institutions, finally, support the dissemination of the internet program in various ways.
|
|
|
|
|
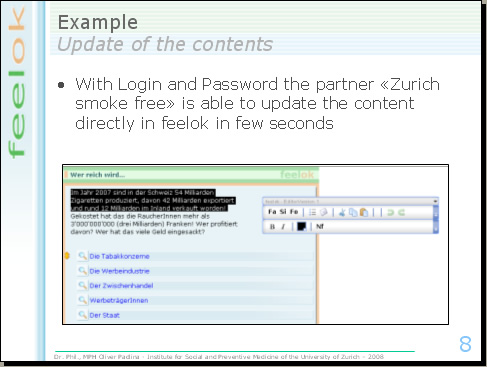
"Zurich smoke free" is responsible for the contents of the smoking prevention program, this means, once a year our contact person checks the content of this intervention. If changes are needed, Zurich smoke free can update the content in a few seconds directly in feelok with their login and password.
|
|
|
|
|
The feelok website is based on the results of scientific studies. We evaluated different aspects of the intervention with diverse methodologies. In the last 10 years we completed 10 studies, for example, we analysed the feasibility of the TTM as a theoretical framework for the stress and smoking prevention program, we investigated the user behaviour of the feelok users, we conducted an effectiveness study about the cannabis prevention program, we evaluated the effectiveness of different dissemination strategies, we tested the didactic tools of feelok and we examined the profile of the feelok users.
|
|
|
|
|
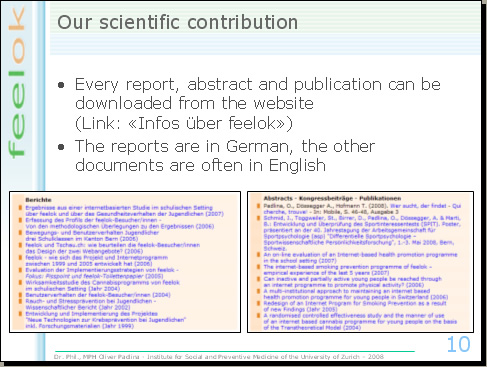
Every report, abstract and publication can be downloaded from the website. The reports are in German, other documents are often in English.
|
| |
| |
|
|
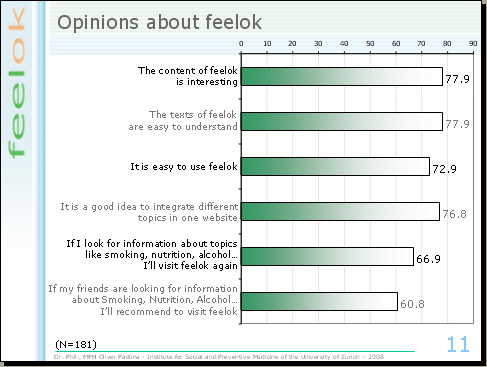
A main question concerns what youths think about feelok. We investigated this subject in different studies and we got consistently similar findings. Between 70% and 80% of the youths appraise the content of feelok as interesting and the texts as easy to understand. They appreciate that the intervention covers different topics and think, it is easy to navigate in the website. Two-thirds plan to visit feelok again, if the topics of the website become relevant to them and will suggest to friends to do the same, if they are looking for information which is covered by feelok.
|
|
|
|
|
feelok is primarily an intervention which was designed for the needs of the school setting. To promote the use of feelok at schools, there is a manual and various worksheets. The manual offers an overview about feelok and contains suggestions how teachers can use the intervention with school classes. With the worksheets, the pupils don't need the support of the teachers to work with feelok. With these worksheets, even teachers who don't feel comfortable to work with Internet are able to make use of feelok in class.
|
|
|
|
|
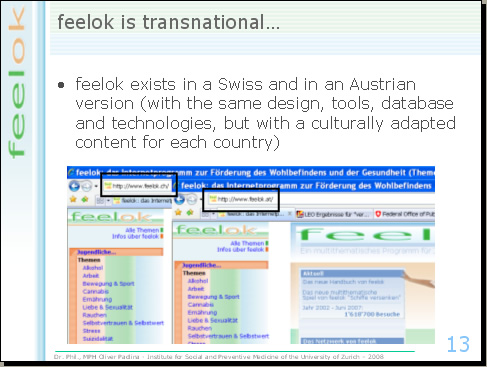
feelok exists in two versions: a Swiss (.ch) and an Austrian version (.at). They share the same design, tools, data base and technologies, but the content is culturally adapted for each country.
|
|
|
|
|
The University of Zurich is responsible for feelok.ch and styria vitalis in Graz is responsible for feelok.at. This collaboration represents a win-win situation. Both institutions share the same intervention. This promotes the exchange of experiences and allows for common projects. feelok also exists in a .de version and we are looking for a partner in Germany who is interested in collaborating with us in order to update the content and disseminate the German version of feelok.
|
|
|
|
|
Our statistics show that feelok is visited every day by 1200 people on average. And about the characteristics of our visitors, our studies always show similar patterns: about 60% of the visitors use feelok in the school setting, 75% are between 12 and 18 years old und 60% are girls.
|
|
|
|
|
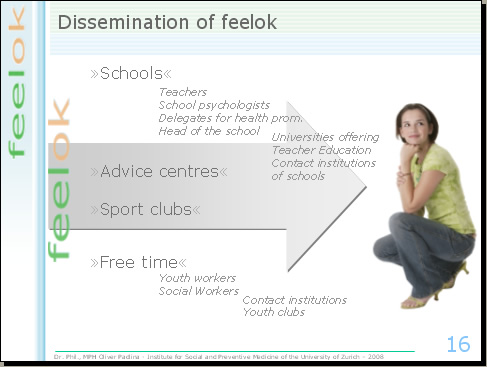
To reach such a number of youths, various dissemination strategies are needed. To promote the dissemination of feelok, we operate in different settings, where youths work and live, and these settings are the schools, advice centres, sport clubs and places where young people spend their free time. Different mediators operate in these settings. For instance to promote the use of feelok in schools we work together with teachers, with school psychologists, with delegates for health promotion and with the heads of the schools. To reach these mediators, we collaborate with the universities offering teacher education courses and with a network of contact institutions in the school field. For every setting we need different strategies to identify the appropriate mediators and the adequate channels to reach them.
|
|
|
|
|
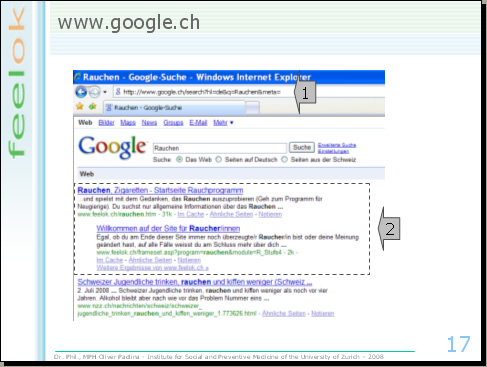
And of course, if you have an internet program, it is also important to have a good positioning in search engines like google. In our case, if you use google.ch and the keyword "smoking", feelok appears in the first two positions. This for two reasons:
1. We keep in mind the roles of google. The keyword "smoking" has for example to appear in the title of the website and in other central positions of the document.
2. Secondly, many websites have a link to the smoking prevention program of feelok. This is an important requisite for a good positioning in google.
|
|
|
|
|
The last information about feelok concerns the budget. The project feelok has been running for 9 years and has generated costs of two millions Swiss francs, this means 1'250'000 Euro. 5 institutions have supported the project financially.
|
|
|
|
|
And now I'll speak about the smoking prevention program and present some findings in this field.
|
|
|
|
|
The first question is, if it is possible to reach young smokers with an internet program. If the answer would be no, we wouldn't need a smoking prevention program.
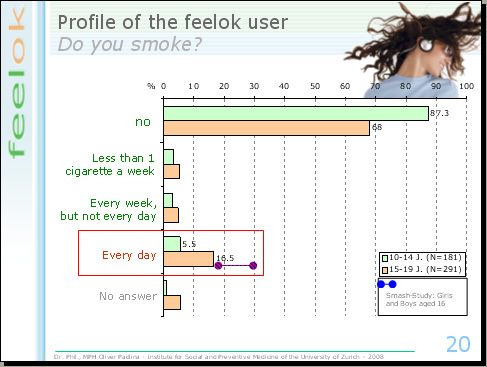
The representative study SMASH (=Swiss Multicenter Adolescent Survey on Health) shows that between 17% and 30% of the young people aged 16 smoke daily in Switzerland. 16.5% of the feelok users are also daily smokers; this means it is possible to reach the target group of the smokers with an internet program.
|
|
|
|
|
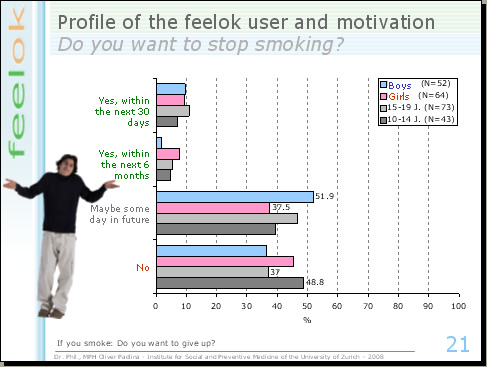
We further found that only 10% of the smokers of feelok are ready to stop smoking within the next 30 days, this is the conclusion of our studies. Approximately 40% don't want to stop smoking and 40% think they may possibly stop smoking some day, but surely not within the next 6 months.
|
|
|
|
|
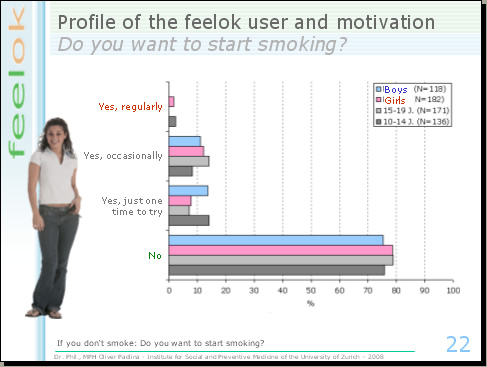
The good side: 80% of the never smokers don't want to smoke; just 10% would like to try it once because they are curious and 10% can imagine to smoke in the future occasionally. These findings demonstrate that young people are located in different stages regarding their smoking behaviour. This suggests that a smoking prevention program should have a stage based theoretical framework.
|
|
|
|
|
In fact, the smoking prevention program of feelok consists of 7 interventions for 7 target groups with different needs. The non-smokers, the curious, the occasional smokers, the smokers without concerns, the smokers, who think, it would be good to give up smoking, the smokers, who want to stop smoking and the former smoker, who may be at risk of a relapse. When the feelok users visit the smoking prevention program, they read the description of the 7 groups and they decide which section is the most adequate for them. If they don't want to choose a stage based intervention, they can click on "you are just looking for general information around the topic of smoking". In this case, they will not get tailored information.
The next question: do the youths work with all stage based sections of the smoking prevention program?
|
|
|
|
|
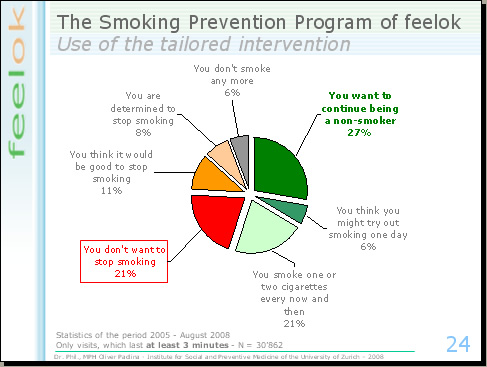
The answer is yes, every stage of the smoking prevention program is addressed by the youths, however with different frequencies. 27% of the visitors work with the content for convinced non smokers. 21% of the youths, however, work with the content for smokers without concerns. The transtheoretical model defines this stage as the stage of precontemplation. For every intervention, it is very difficult to reach the target group of the precontemplator. feelok can do it and the reason, probably, is the dissemination of the intervention in the schools. Young people are motivated, maybe also constrained by teachers, to work with the smoking prevention program. They do it and if necessary, they work also with the section for precontemplators. However, if feelok would be accessed primarily during the young people’s free time, we probably wouldn't able to reach so many precontemplators.
|
|
|
|
|
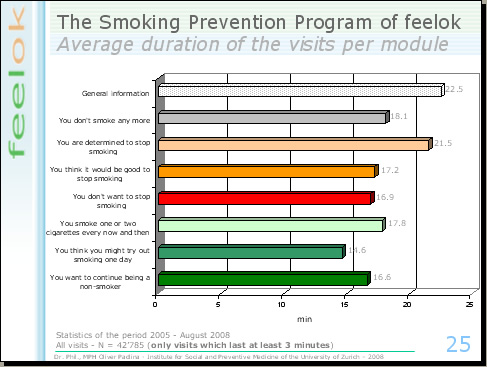
The smoking prevention program also offers a section with general information; this means a section without tailored information. Youths work with this general section for 22 minutes on average. The figure shows the average duration of the visits in the stage based sections: they range from 14 minutes for the smokers with concerns to 21 minutes for young smokers who are determined to stop smoking.
|
|
|
|
|
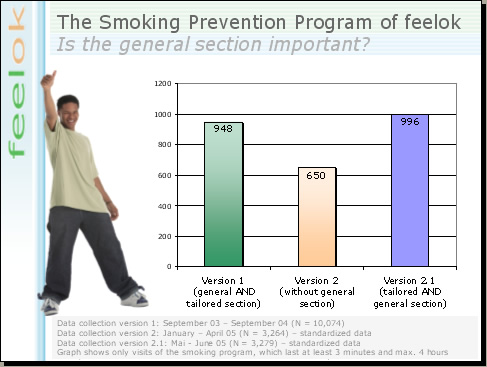
Do we need a section with general information about smoking? This is the next question. Version 1 of the smoking prevention program offered a general section in addition to the tailored interventions. In version 2 we decided to remove the general section. Consequently, we lost 1/3 of the visitors. After the reintroduction of the general section in version 2.1 of the smoking prevention program, the number of visits increased again to similar levels like version 1. The conclusion is that if you don't offer a general section about smoking, you will not be able to reach certain segments of the target group.
|
|
|
|
|
What is the effectiveness of the intervention? Well, for an answer we still have to wait for 6 months. For this reason, I will only present the design of the effectiveness study here.
|
|
|
|
|
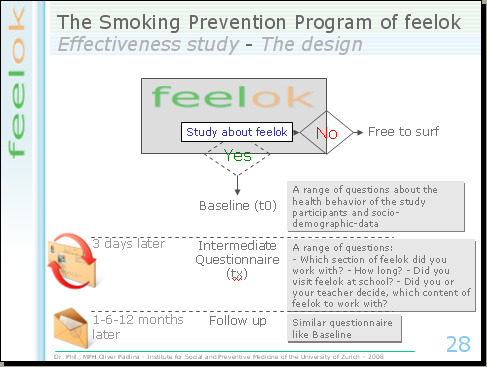
The users were informed about the study on the homepage of feelok. The declared goal of the study was to learn more about the health behaviour of the youths and how they use feelok. In this short description we didn't speak about an effectiveness study; this means, the participants didn't know they participated in an effectiveness study.
The participants of the study completed an internet based questionnaire; this was the baseline questionnaire with questions about their health behaviour and socio-demographic data. Three days later, the participants got an email. We asked them to fill in an intermediate internet questionnaire, which contained questions like: - Which section of feelok did you work with? - How long? - Did you visit feelok at school? - Did you or your teacher decide, which content of feelok to work with? These questions are very important for our study, because we can assign the participants to the experimental and to the control group based on the answers. More details will follow later.
1, 6 and 12 months later the participants get an email with a link to the follow up questionnaire. In this way, we can monitor changes in their health behaviour.
|
|
|
|
|
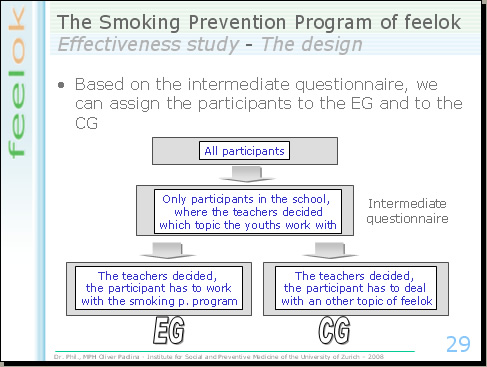
Based on the answers of the intermediate questionnaire, we can assign the participants to the experimental and control group. We will only analyse the data of the participants, who work with feelok in the classes where the teachers decided which topics the youths had to work with. If the teacher decided that the study participant had to work with the smoking prevention program, we assign this participant to the EG. If the teacher decided that the participant has to work with other programs of feelok (for instance the stress program), we assign him to the CG.
|
|
|
|
|
This means: the youths participate in the study. However, they don't know the authentic goal of the study. The teachers participate indirectly in the study. However, they don't know, that they are involved in an effectiveness study and they surely don't know that their decisions form the basis for the assignment of the participants into EG and CG.
|
|
|
|
|
The smoking prevention program is the main application of feelok to promote the abstinence from smoking. However, feelok offers other tools and services to help youths to give up smoking. I give you a short overview:
Young people can ask questions about smoking to experts and they get an answer within three days. In addition, the visitors find in our database which counselling centres are specialised in the field of smoking prevention. Youths who need help can make contact with these centres.
|
|
|
|
|
With the game battleship we deal with health relevant content in amusing way. Youths have to answer questions correctly if they want to shoot at the ships of the computer. The questions are linked to the programs of feelok. In this way, we try through the game to motivate the youths to deal with the content of feelok.
|
|
|
|
|
We interviewed numerous young people, and so we created short video clips about different topics. Teachers can use these clips and the associated worksheets to deal with topics like smoking, alcohol consumption, sexuality etc. For young people who have difficulties reading a lot of text, multimedia approaches may offer better access to work with health related content.
|
|
|
|
|
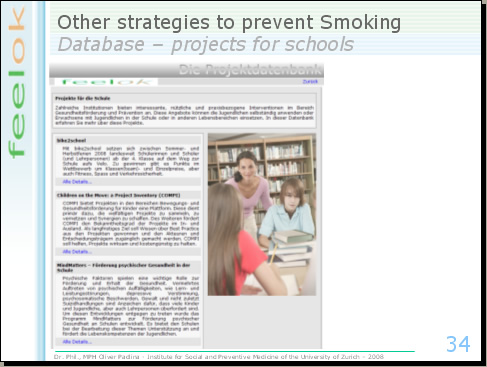
There are a lot of projects in the field of health promotion and of smoking prevention. Common to all projects is the difficult to reach the school setting. For this reason, we integrated a new database in feelok called projects for the schools. Project leaders can use feelok as a platform to inform schools about their own projects. Also for the projects in the field of the smoking prevention, feelok is a new channel to inform teachers about new interventions.
|
|
|
|
|
The tobacco control foundation decided a few months ago to support feelok with the goal to develop the new version of the smoking prevention program. I would like to highlight three aspects of this development.
|
|
|
|
|
First the evaluation
An external institution evaluates the tools of the current version of the smoking prevention program to identify which tools are ok, which have to be removed and which have to be updated. 12 classes participate in the evaluation. The research design consists of qualitative and quantitative methods. During the next weeks, we will discuss with a new task force of experts which ideas we wish to realise within the new version of the smoking prevention program and we will evaluate these new ideas with 6 classes. Based on both evaluations, we will develop the smoking prevention program version 3.
|
|
|
|
|
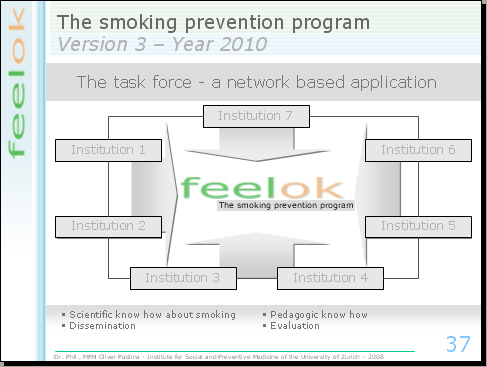
Second interesting point: the task force
The task force consists of representatives of institutions which have a great expertise in the field of the smoking prevention, of the pedagogy, dissemination and evaluation of smoking related interventions. We will develop the new smoking prevention program under supervision of this task group.
|
|
|
|
|
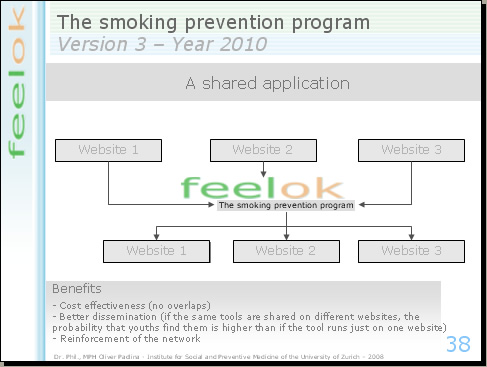
Innovative is the concept of the "shared application". We will integrate in the smoking prevention program attractive tools of other websites, and other websites can integrate tools of feelok in their own platform. With other words, the same tools will run on different websites. This strategy has three benefits:
• Nobody will develop tools, which already exist. In this way, we can use the financial resources for other goals.
• The dissemination. If the same tool runs on different platforms, the probability to reach the target group is higher than if this tool runs only on one website.
• And last but not least: if different institutions share the same tools and services, this reinforces the collaboration within the network.
|
|
|
|